The Climategate Emails describe how a small band of climatologists cooked the books to make the last century seem dangerously warm.
...The Climategate Emails reveal something else, too: the enlistment of the most widely read source of information in the world — Wikipedia — in the wholesale rewriting of this history.
...But the UN’s official verdict that the Medieval Warm Period had not existed did not erase the countless schoolbooks, encyclopedias, and other scholarly sources that claimed it had. Rewriting those would take decades, time that the band members didn’t have if they were to save the globe from warming. Instead, the band members turned to their friends in the media and to the blogosphere, creating a website called RealClimate.org. “The idea is that we working climate scientists should have a place where we can mount a rapid response to supposedly ‘bombshell’ papers that are doing the rounds” in aid of “combating dis-information,” one email explained, referring to criticisms of the hockey stick and anything else suggesting that temperatures today were not the hottest in recorded time. One person in the nine-member Realclimate.org team — U.K. scientist and Green Party activist William Connolley — would take on particularly crucial duties. Connolley took control of all things climate in the most used information source the world has ever known – Wikipedia. Starting in February 2003, just when opposition to the claims of the band members were beginning to gel, Connolley set to work on the Wikipedia site. He rewrote Wikipedia’s articles on global warming, on the greenhouse effect, on the instrumental temperature record, on the urban heat island, on climate models, on global cooling. On Feb. 14, he began to erase the Little Ice Age; on Aug.11, the Medieval Warm Period. In October, he turned his attention to the hockey stick graph. He rewrote articles on the politics of global warming and on the scientists who were skeptical of the band. Richard Lindzen and Fred Singer, two of the world’s most distinguished climate scientists, were among his early targets, followed by others that the band especially hated, such as Willie Soon and Sallie Baliunas of the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, authorities on the Medieval Warm Period. All told, Connolley created or rewrote 5,428 unique Wikipedia articles. His control over Wikipedia was greater still, however, through the role he obtained at Wikipedia as a website administrator, which allowed him to act with virtual impunity. When Connolley didn’t like the subject of a certain article, he removed it — more than 500 articles of various descriptions disappeared at his hand. When he disapproved of the arguments that others were making, he often had them barred — over 2,000 Wikipedia contributors who ran afoul of him found themselves blocked from making further contributions. Acolytes whose writing conformed to Connolley’s global warming views, in contrast, were rewarded with Wikipedia’s blessings. In these ways, Connolley turned Wikipedia into the missionary wing of the global warming movement. The Medieval Warm Period disappeared, as did criticism of the global warming orthodoxy. With the release of the Climategate Emails, the disappearing trick has been exposed. The glorious Medieval Warm Period will remain in the history books, perhaps with an asterisk to describe how a band of zealots once tried to make it disappear.This was followed up by the article entitled Climategate at Wikipedia in which he further highlights:
Since my Saturday column described how Wikipedia editors have been feverishly rewriting climate history over much of the decade, fair-minded Wikipedians have been doing their best to correct the record. No sooner than they remove gross distortions, however, than the distortions are replaced. William Connolley, a Climategate member and Wikipedia’s chief climate change propagandist, remains as active as ever.
How does Wikipedia work and how does Connolley and his co-conspirators exercise control? Take Wikipedia’s page for Medieval Warm Period, as an example. In the three days following my column’s appearance, this page alone was changed some 50 times in battles between Connolley’s crew and those who want a fair presentation of history.
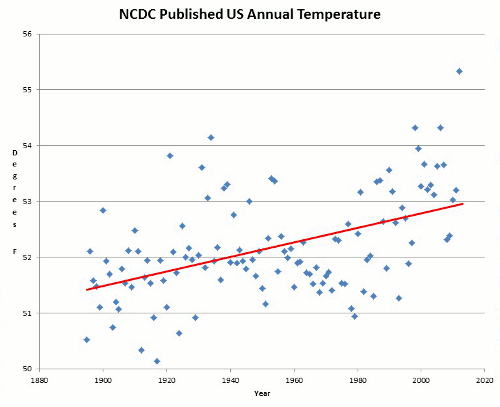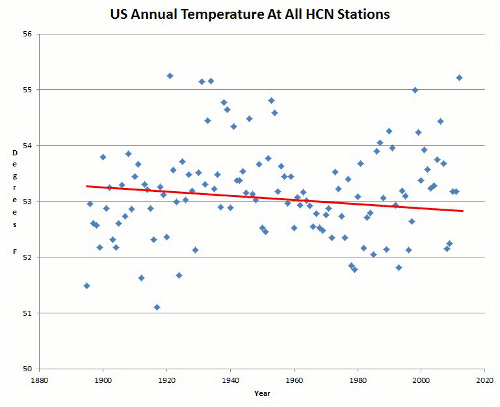
One of the battles concerns the so-called hockey stick graphs, which purport to show that temperatures over the last 2000 years were fairly stable until the last century, when temperatures rose rapidly to today’s supposedly dangerous and unprecedented levels. In these graphs, the Medieval Warm Period – a period of several centuries around the year 1000 – appears to be a modest bump along the way. Before the hockey stick graphs began to be published about a decade ago, scientists everywhere – including those associated with the UN itself – viewed the Medieval Warm Period as much hotter than today. Rather than appearing as a modest bump compared to today’s high temperatures, the Medieval Warm Period looked more like a mountain next to the molehill that is today’s temperature increase.
The hockey stick graphs led to an upheaval in scientific understanding when the UN reversed itself and declared them bona fide. Soon after, the hockey stick graphs were shown to be bogus by a blue-chip panel of experts assembled by the US Congress. The Climategate Emails confirm the blue-chip panel’s assessment – we now know that Climategate scientists themselves doubted the reliability of the hockey stick graphs.
With the hockey stick graphs so thoroughly discredited, you’d think they would become a footnote to a discussion of the Medieval Warm Period, or an object of amusement and curiosity. But no, on the Wikipedia page for the Medieval Warm Period, the hockey stick graph appears prominently at the top, as if it is settled science.
Because the hockey stick graph has become an icon of deceit and in no way an authority worthy of being cited, fair-minded Wikipedians tried to remove the graph from the page, as can be seen here. Exactly two minutes later, one of Connelley’s associates replaced the graph, restoring the page to Connelley’s original version, as seen here.
Battles like this occurred on numerous fronts, until just after midnight on Dec 22, when Connolley reimposed his version of events and, for good measure, froze the page to prevent others from making changes -- and to prevent the public, even in two-minute windows, from realizing that today’s temperatures look modest in comparison to those in the past. In the World of Wikipedia, seen as here, the hockey stick graph, and Connolley’s version of history, still rules.
This bias by Wikipedia was not isolated. In fact the Google readjustment (read hiding) of the number of articles referring to Climategate became known as "Googlegate," such was the level of interference. In Solomon's article Better off with Bing he writes:
This week, Google announced an end to its long-standing collaboration with the Chinese Communists — it will no longer censor users inside China.
That’s good of it. Maybe Google will now also stop using its search engine to censor the rest of us, in the Western countries.
Search for “Googlegate” on Google and you’ll get a paltry result (my result yesterday was 29,300). Search for “Googlegate” on Bing, Microsoft’s search engine competitor, and the result numbers an eye-popping 72.4 million. If you’re a regular Google user, as opposed to a Bing user, you might not even know that “Googlegate” has been a hot topic for years in the blogosphere — that’s the power that comes of being able to control information.
Despite Google’s motto of “Do No Evil,” it has long been controversial and suspected of evil-doing — and not just in its cooperation with China, or in protecting itself by hiding criticism of itself from unsuspecting Google users. In recent months, most of the evil-doing has focused on the Climategate scandal, the startling emails from the Climate Research Unit in the UK that show climate change scientists to be cooking the books.
For many weeks now, readers have been sending me emails describing how Google has been doing its best to hide information relating to Climategate, which has been the single biggest story on the Internet since the Climategate emails came to light on November 19. By Nov. 26, the term had gone viral and Google returned more results for “climategate” (10.4 million) than for “global warming” (10.1 million). As the Climate Scandal exploded, and increasing numbers of blog sites covered it, the number of web pages with Climategate continued to climb. On Dec. 7, Google’s search engine found 31.6 million hits for people who searched for “Climategate.”
Sometime around then, in early December, Google began to minimize the Climategate scandal by hiding Climategate pages from its users. By Dec. 17, the number of climategate pages that a Google search found dropped by almost 10 million, to 22.2 million. One day later Google dropped its find by another 8 million pages, to 14.1 million. By Dec. 23, Google could find only 7.5 million hits and on Dec. 24 just 6 million. And yesterday, when I checked, Google reported a mere 1.8 million climategate pages. See Here.
Bing, in contrast, didn’t make climategate pages disappear. As you’d expect from a search engine that wasn’t manipulating data, search results on Bing climbed steadily until they peaked at around 51 million, where they have remained since. See Here
Starting in late November, Google has been keeping the public in the dark about Climategate in other ways, too. Ordinarily, when people begin keying in their search terms, Google helpfully suggests the balance of their text, through an automatic feature it calls Google Suggests.
At the very beginning of the Climategate scandal, before it became huge, Google Suggests worked as advertised. If someone typed in c-l-i-, Google would have shown them “climategate” on a list of options. Many people, in fact, learned about Climategate this very way, because most major media outlets had not yet picked up on the scandal. As Climategate rose in intensity, the term also rose in prominence on the Google Suggest list — anyone keying in c-l-i would see “climategate” at the top of the list.
But suddenly in late November, for reasons known only to Google, Google often would not suggest “climategate” to those who keyed in c-l-i. Even c-l-i-m-a or c-l-i-m-a-t-e-g-a-t weren’t enough to solicit a suggestion. Bing, in contrast, did not and does not steer users away from climategate — it has consistently suggested “climategate” to those who keyed in c-l-i or even c-l.
For those whom Google can’t steer away from “climategate,” and who key in all 11 letters to learn about the eye-opening emails, Google goes the extra yard in keeping people in the dark — it dishes up a page that trivializes the scientific significance of climategate. Those who click on Google’s “I’m feeling lucky” after asking for “climategate” find themselves on a Wikipedia page entitled “Climatic Research Unit hacking incident” that downplays the content of the emails and focuses on the “unauthorised release of thousands of emails and other documents obtained through the hacking of a server,” the “illegal taking of data,” the “Law enforcement agencies [that] are investigating the matter as a crime,” and “the death threats that were subsequently made against climate scientists named in the emails.”
For those who don’t use Google’s “I’m feeling lucky” feature, Google presents them with this one-sided Wikipedia page as the first item in its search results. Wikipedia actually has a page called “Climategate” that contains damning information about the scientists caught up in the scandal but its own censors won’t let the public see it — anyone who tries to key in “Climategate” on the Wikipedia site will be instantly redirected to the Wikipedia-approved version of climategate, where the scandal is described as nothing more than “a smear campaign.”
Why would Google want to tamp down interest in climategate? Money and power could have something to do with it. Search for Google and its founders and you’ll see that they have made big financial bets on global warming through investments in renewable and other green technologies; that they have a close relationship with Al Gore, that Google CEO Eric Schmidt is close to Barack Obama.
But search for Googlegate and you’ll also see that more than money is at stake. The accusations against Google of censorship are wide-spread, involving schemes to elect Barack Obama, attacks on Christianity (key in “Christianity is” and Google will suggest unflattering completions to the phrase), and political correctness (key in “Islam is” and nothing negative is suggested).
The bottom line? Google is as inscrutable as the Chinese, and perhaps no less corrupt. For safe searches, you’re best off with Bing.












No comments:
Post a Comment